Describe characteristics and concepts of build /deploy tools such as Jenkins, Drone, or Travis CI
In the last post we talked about the concepts of CI/CD, emphasizing the importance of the build phase as part of Continuous Integration process. It is now time to dig deeper on the following CI tools: Jenkins, Drone, Travis and GitLab.
Jenkins
Jenkins is a free automation server (open source) designed to automate parts of the software development process, most notably the building, testing, and deployment of code changes. It is Java based, has a large community and has been out there for a while.
Offering modeLanguage/StructureRootURLVM/Container(self-managed)GroovyJenkinsfilehttps://www.jenkins.io/
Its pipeline is maintained in Groovy format and processed as Groovy script. This is the file Jenkins will look for by default
Here is an example to understand the structure:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
<...>
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
<...>
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
<...>
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
<...>
}
}
}
post{
<...>
}
}
``stages-4 (checkout, build, test and deploy)steps-actions to execute on each of the stagespost-Sections containing actions to execute based on the result of the pipeline (success, failure, always)
Visit this page to learn more about the Pipeline
Jenkins also offers a User Interface for Pipeline visualization called Blue Ocean
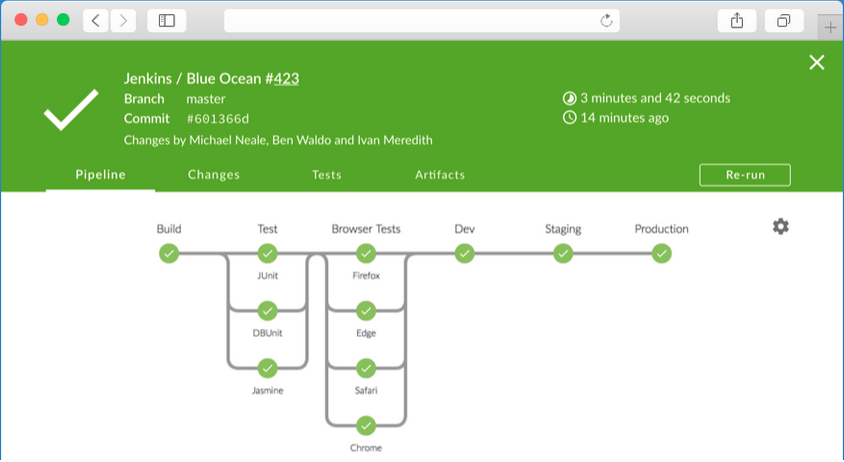 https://www.jenkins.io/blog/2016/05/26/introducing-blue-ocean/
https://www.jenkins.io/blog/2016/05/26/introducing-blue-ocean/
The idea behind it is to improve the developer experience - make it easier to understand the Pipeline, make changes and monitor status and issues arise.
Drone
Built on a container technology. Feature set can be augmented through plug-ins that can work with source control technologies (GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab, etc).
Two versions available - Free for Open Source and cloud service (not free).
Offering modeLanguage/StructureRootURLSaaS/Container(self-managed)YAML.drone.ymlhttps://www.drone.io/
It is written in Go and uses the following .drone.yml structure:
kind: pipeline
name: example
steps:
- name: install
image: node:14
commands:
- npm install
- name: test
image: node:14
commands:
- npm test
- name: deploy
image: alpine
commands:
- echo "Deploying the application"
# Include deployment commands or scripts here
kind-indicate this is a pipeline config (other values could be docker, kubernetes, secret)name -name of the pipelinesteps-indicate individual sections of the pipeline. Each step has its own name, Docker image and commands to execute.
Drones GUI will allow you
Check out this video by Harness to get familiar with Drone and the GUI.
Visit Drone.io to learn more about this tool, plug-ins and to check the documentation.
Travis CI
Integrates very well with Github.com API. Offered as Software-as-a-Service and Open Source projects can be tested for free. VM/Container options are available as well.
Offering modeLanguage/StructureRootURLSaaS/Container(self-managed)YAML.travis.ymlhttps://travis-ci.org
---
language: node_js
node_js:
- "14"
env:
- CI_REG_IMG_APP="my_node_app"
before_script:
- echo "Logging into DockerHub..."
- echo "$DOCKER_PASSWORD" | docker login -u "$DOCKER_USERNAME" --password-stdin
script:
- echo "Building Docker image..."
- docker build -t $CI_REG_IMG_APP .
deploy:
<...>
languageandnode-Defines language to be used and versionsenv-Environment variable definition happens herebefore_script-Contains commands to be executed before running the main build scriptscript-Contains the main build scriptdeploy-Specifies deployment configuration
I’d recommend checking out this video that shows how easy it is to integrate with Github and getting started with Travis.
GitLab
Available Enterprise and Community edition.
Gitlab has many features for DevOps:
- Git Repository
- Docker Image Registry
- Project Board
- CI/CD Pipelines
- Runners
Offering modeLanguage/StructureRootURLSaaS/Container(self-managed)YAML.gitlab-ci.ymlhttps://gitlab.com
---
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
variables:
NODE_VERSION: "14"
before_script:
- npm install -g yarn
- yarn install
build:
stage: build
script:
- yarn build
test:
stage: test
script:
- yarn test
deploy:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploying application..."
# Add deployment commands here
only:
- main
stages-Defines stages of the pipelinevariables -Defines global variables for the pipeline.before-script -Specifies commands to be executed before running any job in the pipelinebuild -Stage to build the application. It executes theyarn buildcommand.test-Stage to run automated tests before deploymentdeploy -Responsible for deploying the application
Here is an example of how this could be represented graphically.
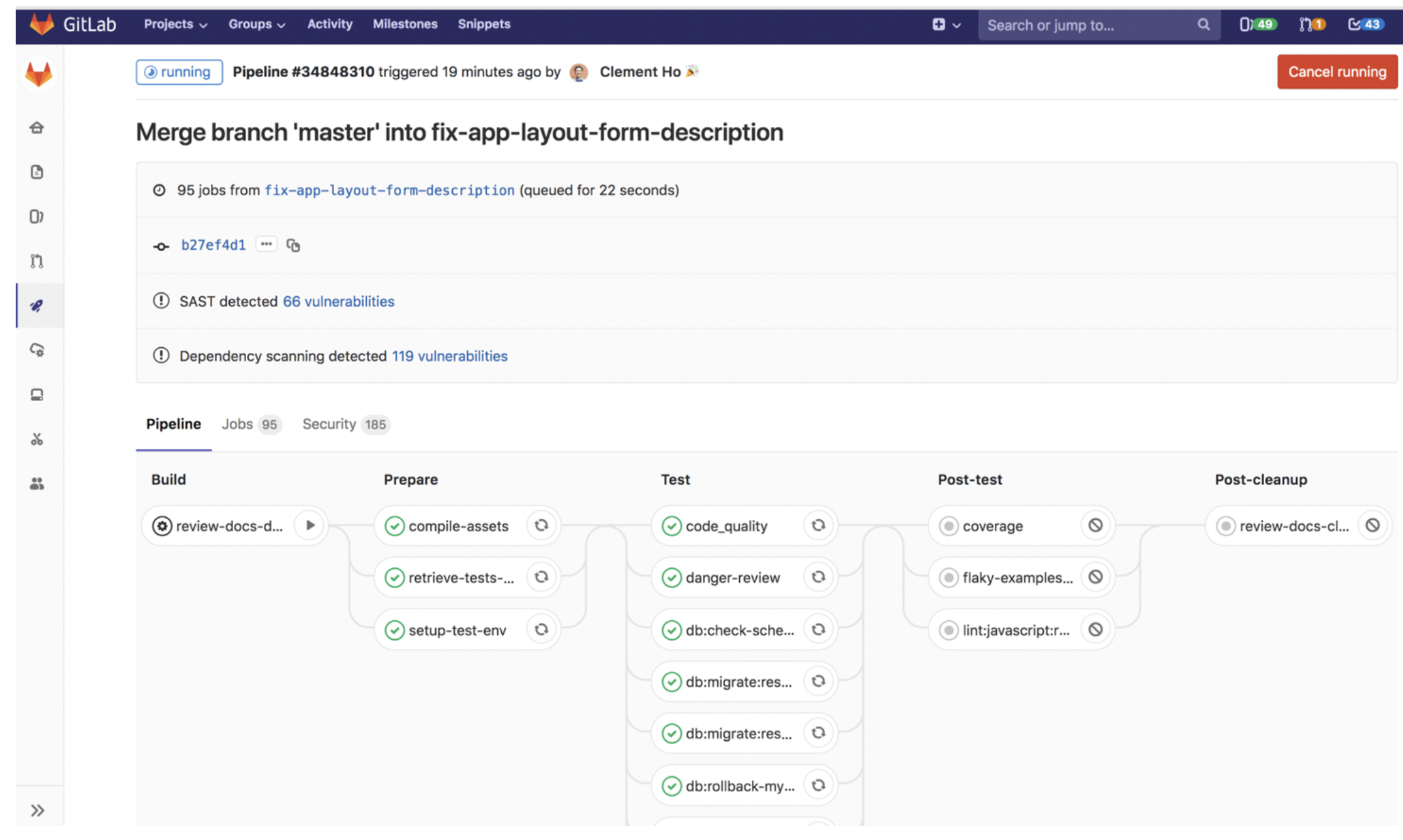
I would suggest exploring some of the tutorials to get familiar with GitLab.